Chromosome structure hercwules
Aggregates of chromomeres are known as chromonemata. Cohesive proteins SMC3 and hRAD21(plays a role in sister chromatid cohesion) are found within chromomeres at high concentrations, and maintain the proper structure of chromomeres. The protein XCAP-D2 is also present at high concentrations within the chromomere, and acts as a condensin component.

How to Pronounce Chromonemata YouTube
1 10nm fibres are seen only by electron microscopy,while chromonema fibres refer to chromatin fibres visible by light microscopy. See this paper. 10nm or 30nm fibres are thus much, much smaller than chromenema fibres. There are likely several layers of organization (like 100nm and 200nm fibres) before you get all the way up to chromenema fibres.

Chromosome Definition, Structure, Types and Function Biology Ideas
What is a chromonemata? Solution Chromosomes: Chromosomes are coiled structures that are present in the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell. Chromosomes contain gene which is said to transfer for generations. Chromosomes contain chromatins which are held together by centromere. Chromatids are coiled structures which contain DNA.
What Is A Chromosome B Fa My XXX Hot Girl
14 Similar questions Q. Chromonemata are embedded in a Q. Each chromonemata contains Q. Chromonemata start associating into bivalent chromosomes during Q. A gaint chromosome with a number of chromonemata is Q. During synapsis the number of thread (Chromonemata) in each chromosome is: View More Introduction BIOLOGY Watch in App

Figure 1 from The Hydration and Dehydration Phenomena in MitosisIV. The chromonemata as natural
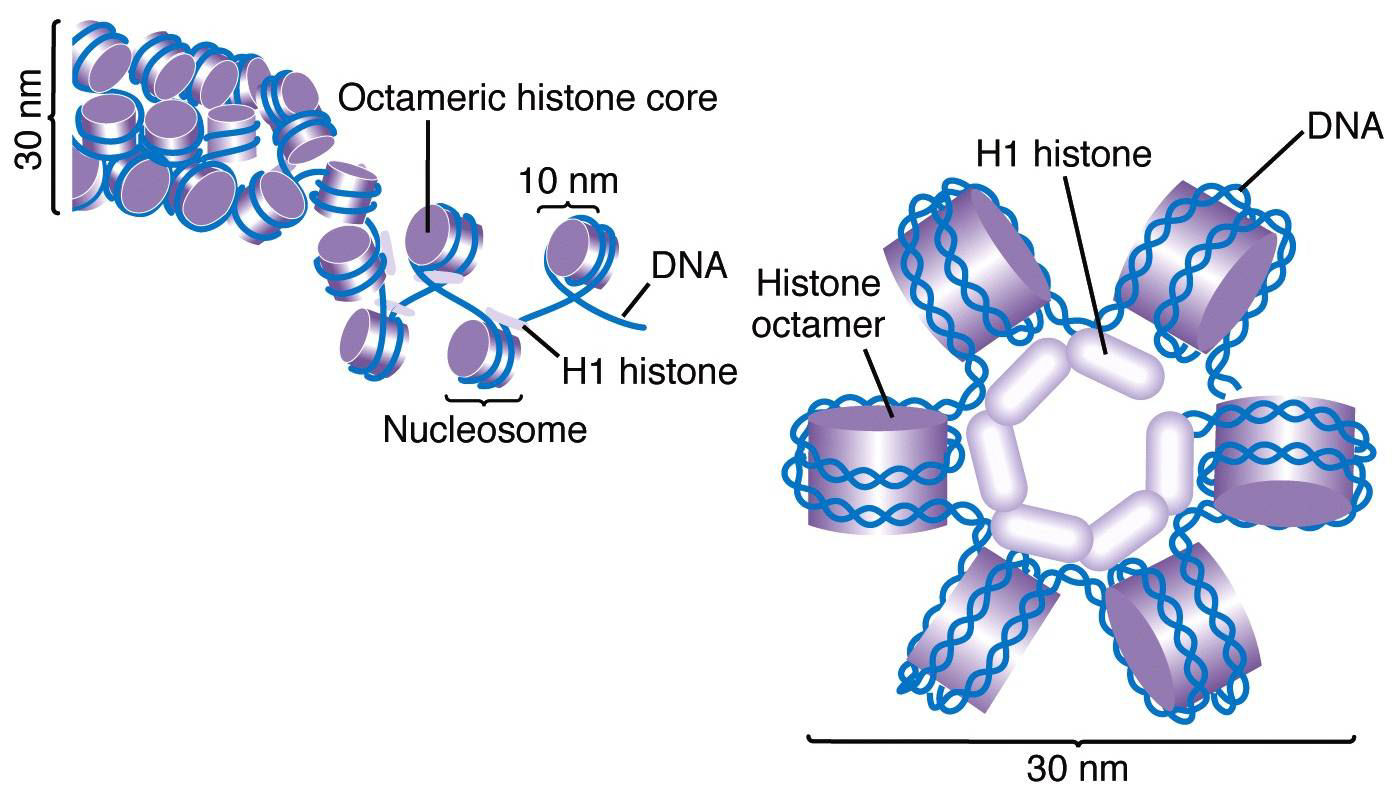
The following levels of DNP compaction in mitotic chromosomes are suggested: a 10-nm nucleosomal fibril, a 25-nm nucleomeric fibril, and the chromonema, a fibrous structure, about 100 nm in diameter, composed of chromomeres. Interphase nuclei also contain structures which are morphologically similar to the chromomeres of mitotic chromosomes.
Pasta Is Made Up Of Wholesale Shop, Save 61 jlcatj.gob.mx
The chromonema is the carrier of the genes. They also help in maintaining the proper structure of chromomere. The chromonema appears to be like a mass of coiled threads at the beginning of the cell division. The chromonema bears several knot or beaded structure which is called chromomere. These granules are present at regular intervals.

Col SEM of giant chromosome from salivary gland Stock Image P657/0014 Science Photo Library
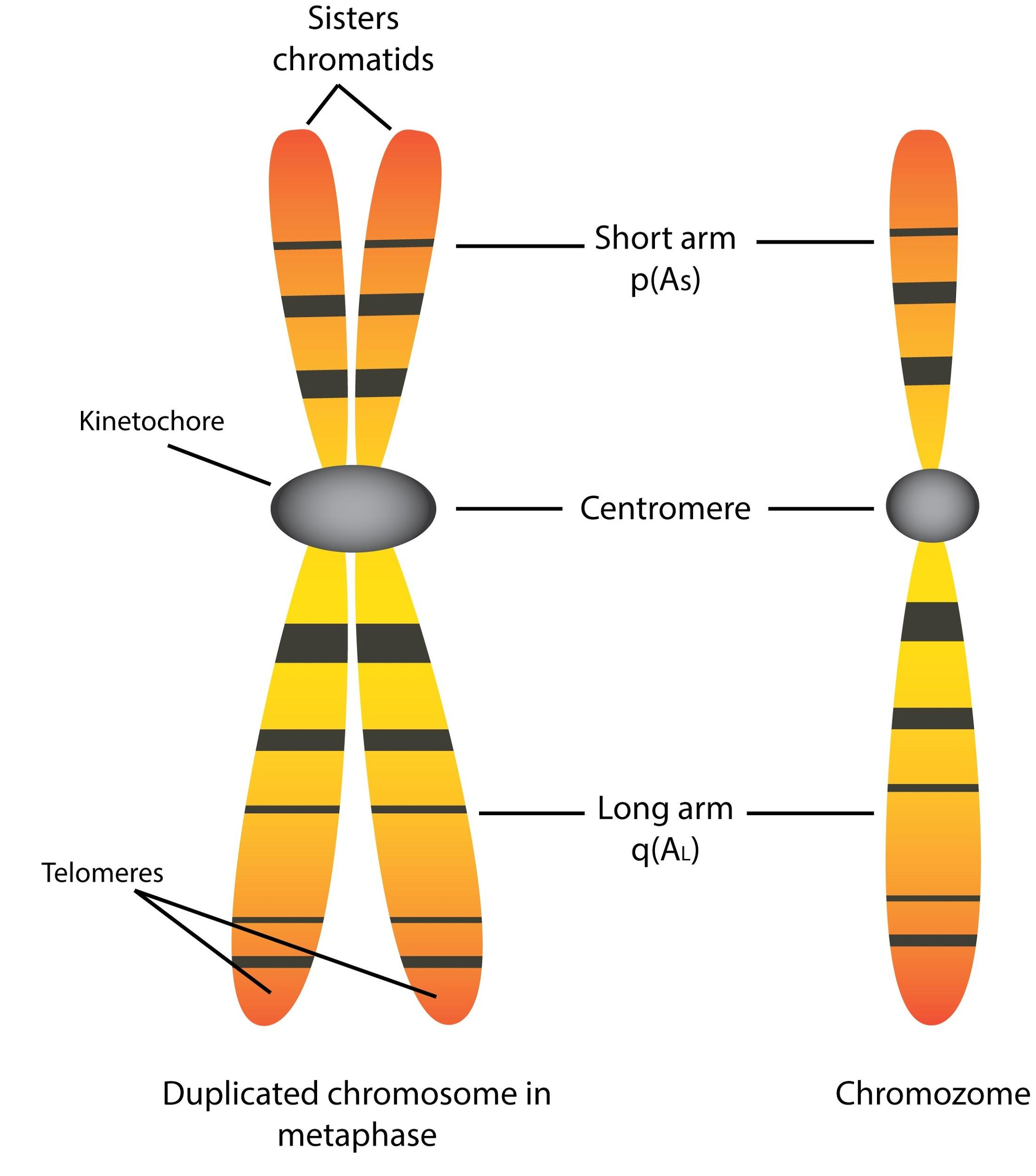
Human karyotype is a representation of the chromosomes present in a human cell. A human cell has 46 chromosomes of different shapes and sizes. Out of the four types of chromosomes that we have discussed so far, three can be observed in our human karyotype. Telocentric chromosomes are absent in humans.

PlantFiles Pictures Xeronema Species, Poor Knight's Lily (Xeronema callistemon) by mrporl
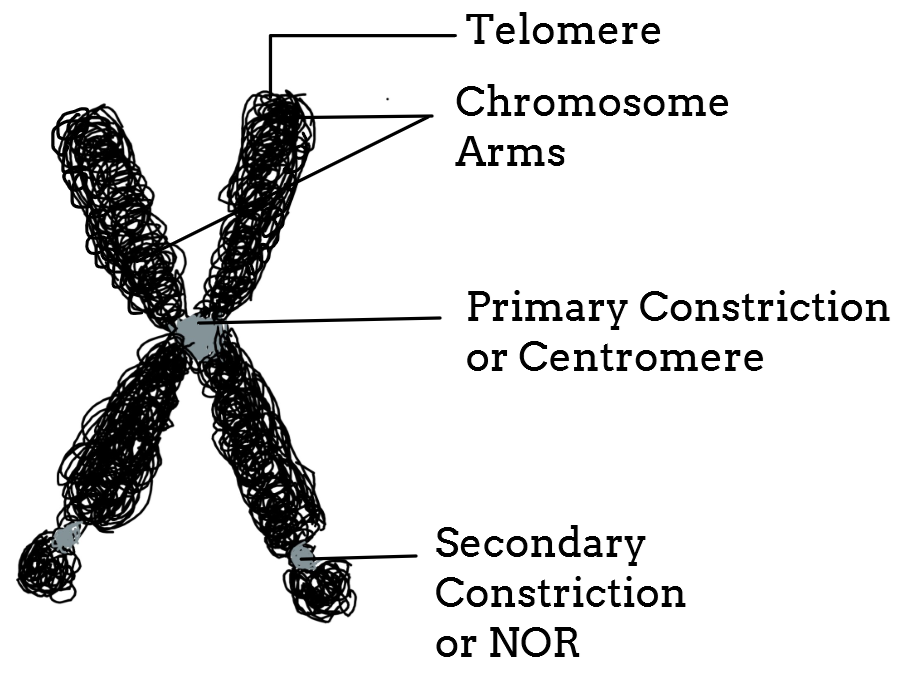
Chromonemata is the gene-bearing structure of a chromosome. Sometimes (in interphase), bead-like accumulations of chromatin material are visible along the chromosomes. These are termed as chromomeres. These are regions of tightly-packed DNA. Usually, the centromere lies within the primary constriction (thinner chromosomal segment).

Pin on NZ Native grasses
chro·mo·ne·ma·ta ( krō'mō-nē'mă, -ma-tă ), The coiled filament in which the genes are located, which extends the entire length of a chromosome and exhibits an intensely positive Feulgen test result for DNA. Synonym (s): chromatic fiber [chromo- + G. nēma, thread] Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012 chromonema (krō′mə-nē′mə)
What are chromonemata and chromomeres?
chromonema Quick Reference (pl. chromonemata) cytological term for 1 all of the threads which make up the nuclear reticulum. 2 any of the smallest strands of DNA in a chromosome or chromatid. 3 a twisted chromatid thread within the chromosome. [.] From: chromonema in Oxford Dictionary of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology »
Describe the structure of the chromosome with a suitable diagram.
chro·mo·ne·ma·ta ( krō'mō-nē'mă, -ma-tă ), The coiled filament in which the genes are located, which extends the entire length of a chromosome and exhibits an intensely positive Feulgen test result for DNA. Synonym (s): chromatic fiber [chromo- + G. nēma, thread] Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012 chromonema (krō′mə-nē′mə)

Xeronema callistemon Native garden, Trees to plant, Plants
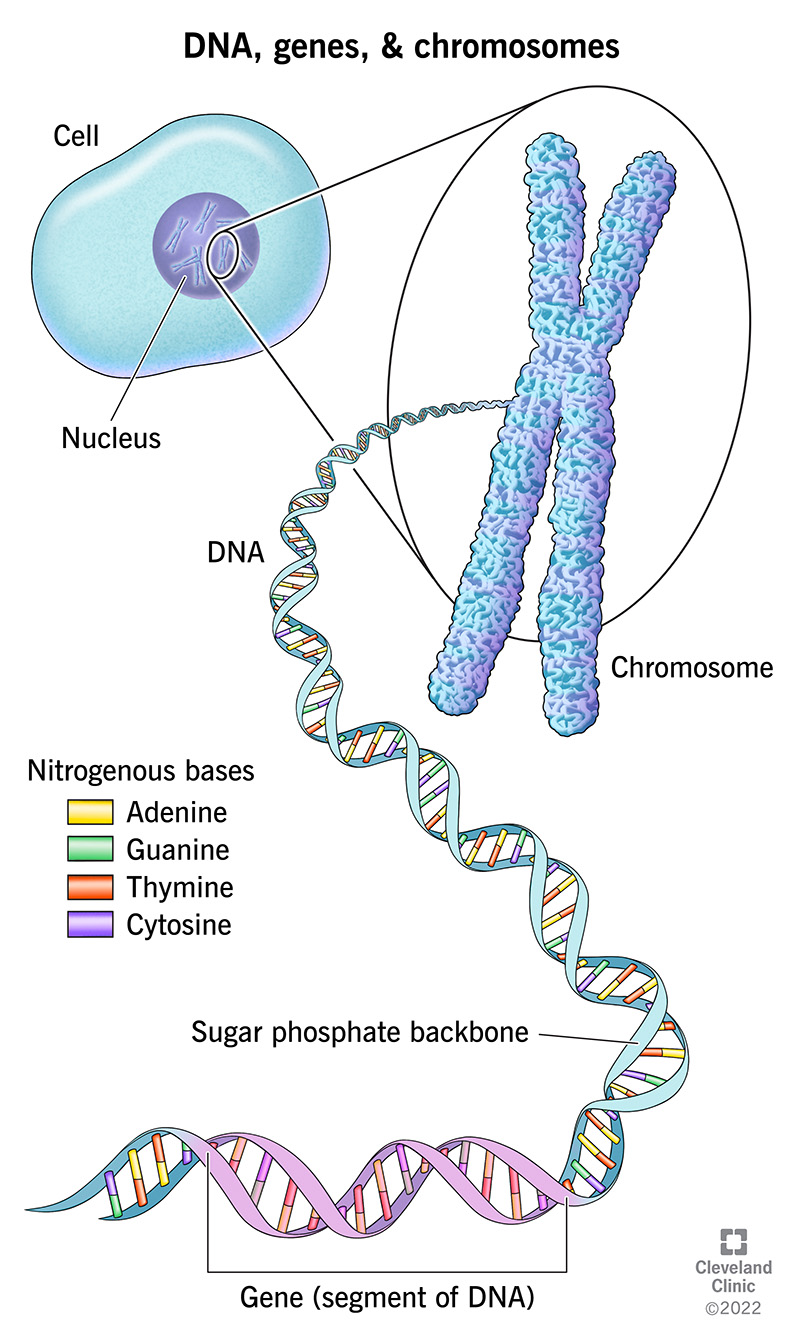
What is the Chromosome structure? How is DNA packaged into chromosomes and describe the structure of a chromosome? The general structure of somatic chromosomes can be studied best at the metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. Each comprises the following parts: Pellicle and Matrix Chromonemata (Chromatid during Metaphase) Chromomeres Centromere

Xeronema callistemon (Xeronemataceae) image 80089 at PhytoImages.siu.edu
Chromonema was first of all observed by Baranetzky in 1880, in the pollen mother cell of Tradescantia, and was called chromonema (singular) by Vejdovsky in 1912. At metaphase each chromosome consists of two symmetrical structures, the chromatids, each of which contains a single DNA molecule.

Xeronema Springvale Garden Centre
What are Chromosomes? Structure of a Chromosome Pellicle Matrix Chromonemata Centromere Secondary Constriction or Nucleolar Organiser Telomeres Types of Chromosomes A. Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes B. On the Basis of Number of Centromeres C. On the Basis of Location of Centromere Prokaryotic Chromosomes Eukaryotic Chromosomes a. Nucleosomes

Chromatin, chromosome, chromatid, chromonema, chromonemata,chromomere YouTube
noun chro· mo· ne· ma ˌkrō-mə-ˈnē-mə plural chromonemata -ˈnē-mət-ə : the coiled filamentous core of a chromatid

Xeronema callistemon (Poor Knight's Lily) Kat's Garden
Chromatin, chromosome, chromatid, chromonema, chromonemata and chromomere- these are sound very similar but are actually different things. These terms are ve.